Dairy Product Price Inflation a Mixed Bag, Still Lagging Overall Food Inflation

All parts of the U.S. economy and at least 44 other nations throughout the world are experiencing high rates of inflation due to several global factors including the COVID-19 pandemic, ongoing supply chain woes, rising wages amid labor shortages, and Russia’s war with Ukraine, which has thrown global energy, food and fertilizer markets into disorder. Here in the U.S., Americans are experiencing the highest rates of inflation across the economy in 40 years. The year over year consumer price index (CPI) registered 8.6% in June. Meanwhile, the Reuters/University of Michigan Consumer Sentiment Index hit an all-time low of 50.2% in June – the lowest recorded level since the survey began in 1978.
While gas and diesel prices have left many feeling sticker shock, Americans are also seeing once-in-a-generation price spikes at the grocery store. Some news reports have pointed to dairy products like a gallon of milk as “soaring” or “spiking” or “skyrocketing”. The truth is a gallon of conventional milk is up 89 cents this year, according to USDA. Prices vary across the country, so a consumer may pay $2.71 per gallon in Louisville or as much as $6 in Kansas City. And when we look at how inflation has affected dairy in comparison to other food products, the picture is mixed, with price increases falling below average food CPI.
Between 1913 and 2022, food experienced an average inflation rate of 3.2% per year. But food inflation accelerated for the 12 months ending May 2022 to 10.1%, the biggest jump since 1981. Retail food prices have taken the brunt of inflation, logging an increase of 12% over the past year. Overall, prices for dairy foods are up 11.8% through May 2022 when compared to May 2021, falling in the middle of the pack among food categories such as eggs (up 32%) and fruits and vegetables (up 7.5%).
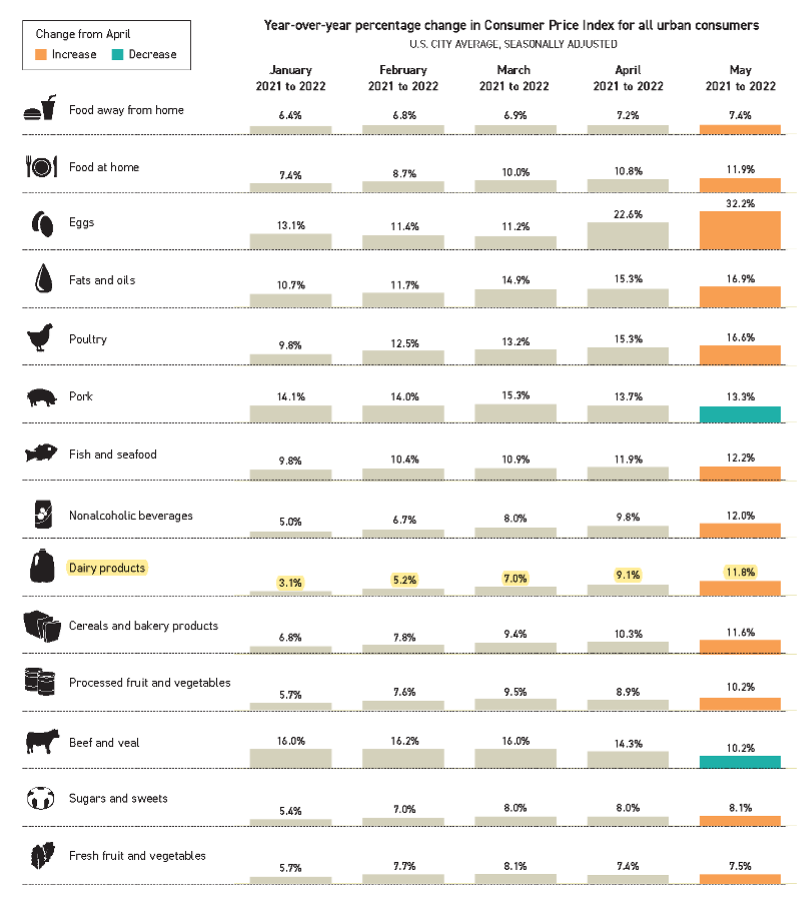
The reasons for retail price inflation are straightforward: higher wholesale prices for several inputs, including milk, energy, packaging materials, ingredients like sweeteners and cultures, and more. USDA forecasts farm-level milk prices to increase between 30-33% and wholesale dairy prices between 14-17% in 2022. Then add the general factors squeezing the economy: labor, wages, war, transportation. Then add something of good news—strong demand for dairy products that has carried through, to some extent, from the pandemic.
But when we step back and look at food price inflation in 2022, from January through May, the data show dairy continues to be a good buy at retail and is near the bottom of the list among all food categories. In fact, overall food inflation logs an increase of 8.7% year to date, year over year; but for dairy, that figure is 7.2%.
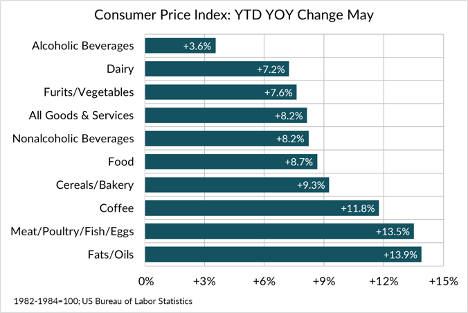
It’s true that retail price gains for dairy still lag wholesale price gains, but the farmgate price of milk has—as many analysts have noted of late—begun to plateau. Let’s take a deeper dive into dairy foods prices.
Wholesale Prices
Class I Milk
- $23.32 per hundredweight YTD, +45% YTD YOY
CME Spot Block Cheddar
- $2.15 per pound YTD, +28% YTD YOY
CME Butter
- $2.76 per pound YTD, +66% YTD YOY
What can we expect for the rest of 2022?
Signs point to inflation cooling from its red-hot January-June peak. As of July 7th, Gasbuddy reports that regular gasoline prices are $3.99 at more than 2,500 locations across the continental United States—a major comedown from the $6 and $7 highs seen in early June. The job market remains strong, too. The U.S. unemployment rate dipped to 3.6% in May, near a 50-year low reached in early 2020. And the gap between available workers and available jobs is large — only 5.94 million unemployed for 11.40 million job openings – which will continue to keep wages on the high side to attract workers.
According to Fortune magazine this week: “… falling commodity prices, a cooling housing market, slowing consumer spending, and sinking forward-looking inflation expectations are all potential indicators that the U.S. economy is entering the beginning of the end of the post-COVID inflationary era.”
Challenges will remain, especially for those already struggling to make ends meet. Americans will continue to rate inflation as the nation’s top problem until prices begin to retreat at the grocery store and gas pump.