Presynch, Ovsynch, ReSynch

Breeding cows based on visual heat detection is important in reproductive management programs on almost all dairies; however, relying solely on visual heat detection can result in poor reproductive performance.
Synchronization protocols have been incorporated into reproductive management programs by most U.S. dairy farms. These protocols have generally consolidated into a few management options depending on if producers want to breed cows based on visual heat versus timed artificial insemination (AI). In general, these protocols fit into one of three categories: presynchronization, Ovsynch and resynchronization.
PRESYNCH
Presynchronization strategies that combine GnRH and prostaglandin increase the number of pregnancies generated by each AI service by initiating ovulation in cows that aren’t cycling and by increasing the proportion of cows that synchronize during an Ovsynch protocol.
There are two fundamental presynchronization strategies:
- Using prostaglandin. This includes two treatments 14 days apart, with the first GnRH treatment in an Ovsynch protocol occurring 12 days after the last prostaglandin treatment. There are two limitations to this protocol. Prostaglandin does not affect anovular cows, and follicular growth is not tightly synchronized after two sequential prostaglandin treatments.
- Using a prostaglandin, GnRH combination. Producers can go one of two ways: a double Ovsynch program, where GnRH is administered followed by prostaglandin seven days later and a second GnRH three days after that; or a variation that drops off the first GnRH treatment. A timed AI program can start seven days after the last GnRH treatment in either case.
OVSYNCH
A number of experiments have compared various timings of the treatments within the Ovsynch protocol as well as timing of AI relative to the last GnRH treatment, which can lead to differences in pregnancies per AI. Chart 1 shows four OvSynch programs.
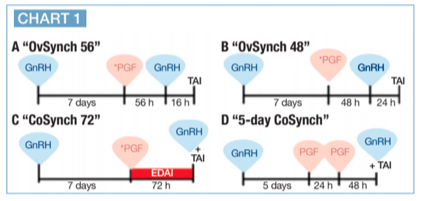
Inclusion of a second prostaglandin treatment 24 hours after the first in a 7-day Ovsynch protocol improves pregnancies per insemination, particularly in older cows. Also, timing of AI relative to a synchronized ovulation affects conception.
RESYNCH
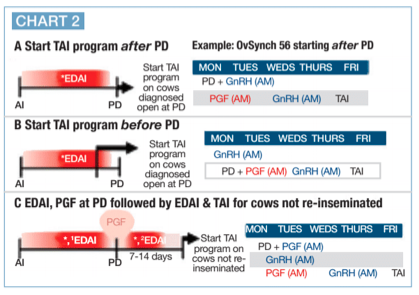
Chart 2 shows three resynchronization programs. Although all three options include detection of estrus and AI after an initial AI, some farms choose to minimize use of AI based on visual heats and submit nearly all cows to a timed AI program. In this scenario, the primary emphasis is on protocol compliance.
Including visual heat detection after an initial AI can increase 21-day pregnancy rates by increasing the AI service rate. Keep in mind this requires two management systems: one for the timed AI protocol, and the other for daily heat detection and AI. Nonetheless, most all herds’ high pregnancy rates submit all cows to timed AI after a fertility program, inseminated any cows seen in heat after first timed AI, and then submitted cows not detected in estrus and diagnosed not pregnant to a Resynch protocol.
It is important to clarify there is not one right way to approach reproductive management on all dairy farms. Each farm must implement a plan to submit cows for first AI and return nonpregnant cows to AI service to boost 21-day pregnancy rate. The Dairy Cattle Reproduction Council has a list of protocols for use on your operation. It can be found at www.dcrcouncil.org.
Paul Fricke is a professor of animal science at the University of Wisconsin-Madison. His research focuses on the biology underlying the many reproductive problems of dairy cattle.
For more on this topic, read: